Joel Breman, Who Helped Stop an Ebola Outbreak in Africa, Dies at 87
Dr. Joel Breman, a specialist in infectious diseases who was a member of the original team that helped combat the Ebola virus in 1976, died on April 6 at his home in Chevy Chase, Md. He was 87.
His death was confirmed by his son, Matthew, who did not specify a cause.
“We were scared out of our wits,” Dr. Breman, recollecting his pioneer mission, told a National Institutes of Health newsletter in 2014, as a new and even deadlier Ebola outbreak raged that year.
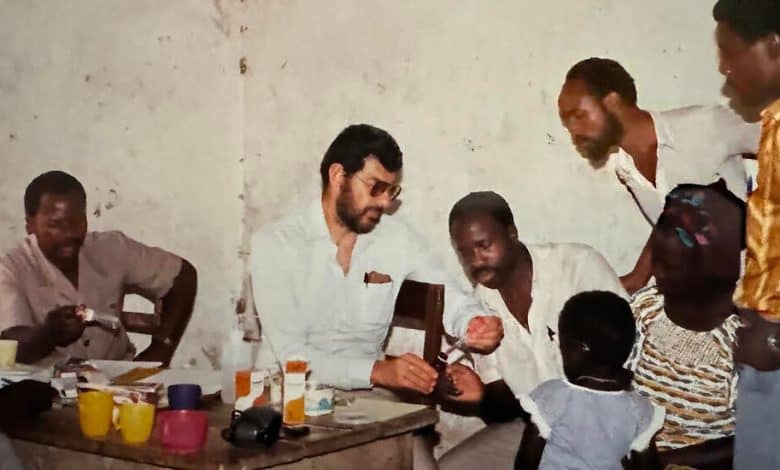
Nearly 40 years earlier, his team of five had just landed in the interior of what is now the Democratic Republic of Congo, at a remote Roman Catholic mission hospital. They were up against a viral infection that had no name, whose origin was unknown, and that was accompanied by high fever and bleeding that led to a painful and quick death.
Dr. Breman, dispatched by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, had only what he described to the N.I.H. as “the most basic protective equipment” against the disease, in contrast to the full-body spacesuit-like gear that was standard in the later outbreak. He and others on the team, laboring in intense heat and bitten by sand flies, “developed rashes and didn’t know if we would catch the virus too,” he said.
But he calmly began deploying the techniques he had honed on earlier missions to Africa, on anti-smallpox initiatives in Guinea and Burkina Faso. He interviewed patients and witnesses, traveling from village to village and going from house to house. He and his colleagues, he recalled, soon determined that the infection was “spread by close contact with infected body fluids,” and that it had been propagated at a rural hospital that was using unsterilized needles.
Over a long career, much of it spent at the Centers for Disease Control, the World Health Organization and the National Institutes for Health, Dr. Breman worked to stamp out deadly tropical diseases like smallpox, malaria and Guinea worm. But that initial Ebola outbreak, he told an interviewer in 2009, “was the scariest epidemic of my entire medical career and possibly of the last century.”